Purpose of the Heat Recovery Ventilator (HRV)
 Every house needs ventilation. Older houses get their ventilation from air leakage, but most modern houses are now tight enough that a mechanical ventilation system is needed.
Every house needs ventilation. Older houses get their ventilation from air leakage, but most modern houses are now tight enough that a mechanical ventilation system is needed.
Why do houses need ventilation? There are five main reasons:
- People need about 8 litres per second (fifteen cubic feet per minute) of reasonably clean air for health and comfort. We ingest air with about 380 parts per million of CO2 (the outdoor CO2 level) and our lungs reject carbon dioxide into the air that we exhale. The air exhaled in our breath is loaded with carbon dioxide-it has about 40,000 parts per million or 4% CO2. If you recycled that exhaled breath directly back into your lungs, you would soon be overcome with carbon dioxide poising. This is essentially what happened in the Black Hole of Calcutta, when a large number of people died in a confined space. Anesthesiologists controlling carbon dioxide in operating room patients is a key concern. Gases are expensive and are recycled back into the patient. The carbon dioxide laden air is put through a scrubber to remove this gas. On submarines and spacecraft, scrubbers are also used to minimize the amount of expensive fresh air. Inside houses and most buildings, carbon dioxide levels should generally be below about 1000 parts per million. If the level is higher it is usually a sign of inadequate ventilation (or a blocked chimney.)
- Humans must have ventilation to get rid of moisture that the body emits. Sedentary adults release about 0.1 kilogram (0.1) litres of moisture per hour, partly through breathing and partly through skin evaporation. Cooking, bathing, floor washing, etc. all contribute additional moisture to the air. One of the common signs of inadequate ventilation in a home with high humidity is condensation on the windows
- It dilutes the air of body odour, perfumes, deodorants, cooking odors etc.
- It removes the off gassing from building materials. The paints, floor coverings, furniture, cabinets etc. all emit some volatile organic compounds, and these should be diluted by adequate ventilation.
- It ensures adequate combustion air for furnaces, boilers, water heaters, fireplaces etc. When any fuel burns sufficient air must be supplied or deadly carbon monoxide can readily occur.
How an HRV works:
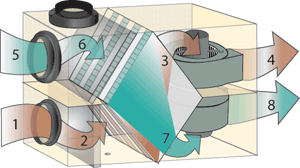 Stale air from the kitchen and bathrooms flows:
Stale air from the kitchen and bathrooms flows:
- Through exhaust grills and ductwork into the HRV.
- Through a washable filter.
- Through the HRV heat transfer core.
- The exhaust air fan quietly moves the stale air through an outdoor hood to the outside.
Fresh Outdoor Air flows:
- Through an outdoor hood into the HRV.
- Through a washable filter.
- Through the HRV heat transfer core.
- The fresh air fan quietly moves the outdoor air through fresh air ductwork and grills (or heating ductwork and registers) to the living areas.